Addressing the chaos of traditional address formats can be overwhelming. While every address points to a specific location, the way these addresses are structured often varies, making them hard to organize. Without a geospatial context, an address loses much of its relevance.
This is where ArcGIS-based LLM models step in. With the power of Large Language Models (LLMs), there’s a smarter way to fix it. This simple workflow helps clean, normalize, and structure chaotic address data into a clear and normalized format making them ready for mapping and smarter decision-making.
By streamlining the complex process of organizing and standardizing addresses, ArcGIS-based LLMs make the task faster, more accurate, and less error-prone, empowering businesses, governments, and service providers to manage locations with greater precision. In short, they provide a smarter, data-driven solution to the long-standing challenge of inconsistent address data.
Why Address Normalization Matters and How ArcGIS Makes It Possible?
Address normalization refers to the process of converting free-form or inconsistent address entries into a structured format suitable for geocoding and analysis. Large Language Models (LLMs) trained in large corpora of text data can interpret and restructure incomplete or incorrect address strings using contextual understanding.
ArcGIS Pro now supports model extensibility, allowing integration with a variety of Large Language Models (LLMs) such as Gemini, GPT, and others. Users can build custom deep learning packages (DLPKs) that connect to these LLMs and combine them with native NLP geoprocessing tools. This enables AI-powered workflows like address normalization directly within the ArcGIS environment.
Workflow in ArcGIS Pro
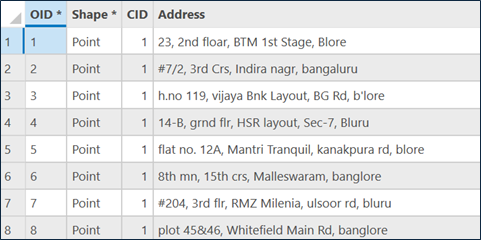
Assume that you’re a telecom provider, and customers have uploaded their addresses while signing up for a new connection. But like most real-world data, the addresses came in all kinds of formats – some had abbreviations, others had spelling mistakes, and many were missing key location details.
To sort this out, we used ArcGIS Pro’s model extensibility feature to bring in the power of a Large Language Model (LLM) like GPT.
Here’s how we set it up:
- Python Function – This defined what the model should do. It included the connection to the LLM through an API, along with other details like the model’s name and how the address should be cleaned.
- Esri Model Definition File – This file told ArcGIS how to run the model. It also included examples and prompts to guide the model in giving better results.
These two pieces were bundled into a. DLPK (Deep Learning Package) model that works inside ArcGIS ecosystem.
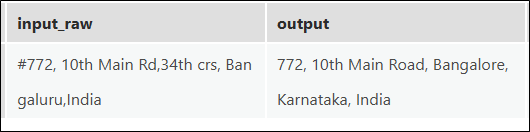
We tested it with a sample address and obtained the following result: “#772, 10th Main Rd, 34th Crs, Bengaluru, India”
Then, using the Transform Text Using Deep Learning tool, we selected the survey data, gave the prompt and then ran the model.
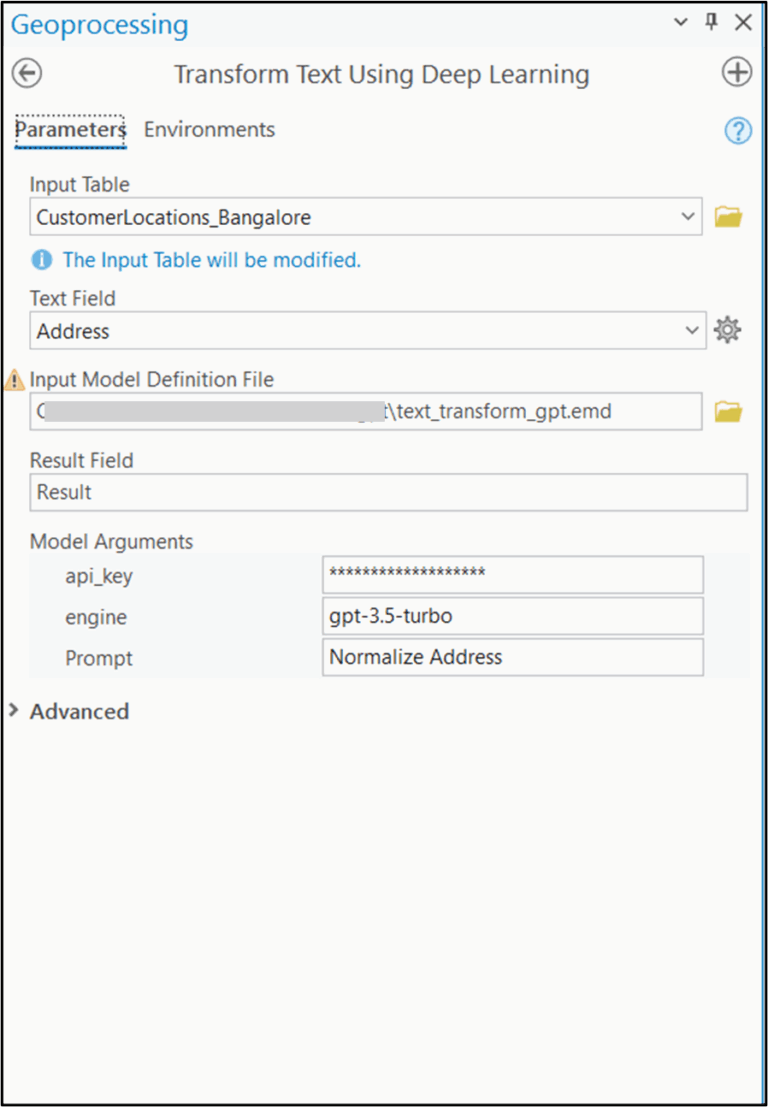
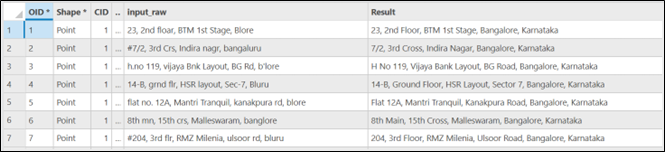
The results were impressive. The model gave us clean, complete, and corrected versions of each address—fixing spelling, expanding short forms, and even filling in missing city names.

Accurate address data is the backbone of geospatial analysis, powering everything from city planning and service delivery to location-based decision-making. Managing messy addresses has long been a challenge, slowing down mapping and analysis. Turning messy, unstructured addresses into accurate, map-ready data used to be a complex task. Now, with ArcGIS and LLMs, this transformation is streamlined and precise.
This workflow highlights the power of ArcGIS Pro and LLMs to enhance geospatial operations whether for city surveys, customer records, or any location-based task, improving the accuracy, consistency, and usability of address data across project.
“Why struggle with messy data when you can let ArcGIS and LLMs do the heavy lifting?”

Sreebhadra is a Senior Engineer and works on translating GeoAI capabilities into practical ArcGIS solutions.