Indian utilities are under pressure
Demand growth, aging infrastructure, climate volatility, and regulatory expectations for reliability and safety, is placing them under pressure. Next‑gen asset management, powered by AI (Geo-AI) and IoT telemetry, is helping utilities transition from reactive maintenance to predictive, risk‑aware, and resilient operations.
With ArcGIS as the spatial digital backbone—combining ArcGIS Utility Network, ArcGIS Real‑Time/Velocity, ArcGIS Pro, ArcGIS Enterprise, and analytics tools like ArcGIS Insights and GeoAI in ArcGIS— utilities can consolidate asset data, stream information from IoT devices, model network connectivity, and drive actionable decisions across the organization.
Why Resilience Needs AI + IoT + GIS
- Spatial context matters: Failures cascade along connected assets (feeders, mains, pipelines). GIS models topology and connectivity so AI can learn where and why risk propagates.
- Signals at scale: Sensors (SCADA, smart meters, vibration, temperature, pressure, lidar, drones) produce high‑frequency streams. IoT + GeoAI turns these signals into real‑time situational awareness.
- Decision automation: From anomaly detection to prioritized work orders, AI closes the loop into EAM/CMMS and Field Apps for faster, safer interventions.
- Regulatory & ESG: Proactive risk reduction lowers SAIDI/SAIFI, leak rates, non‑revenue water, methane emissions, and improves public safety.
The Esri India Approach
A Spatially‑Enabled Asset Intelligence Stack
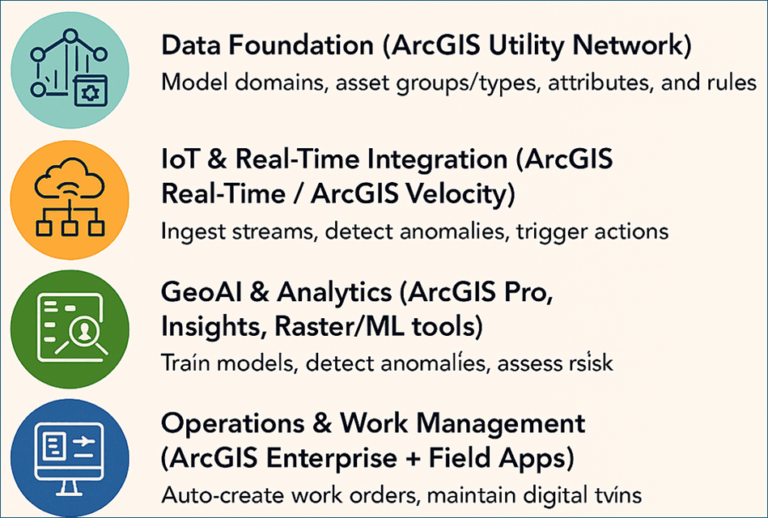
1) Data Foundation (ArcGIS Utility Network):
- Model domains, asset groups/types, attributes, contingent values and rules for electric, gas, water, and telecom.
- Maintain authoritative connectivity, containment, structural attachment, and traces (e.g., upstream/downstream, isolation, outage impact).
- Govern versions via branch versioning for safe multi‑team edits.
2) IoT & Real‑Time Integration (ArcGIS Real‑Time / ArcGIS Velocity):
- Ingest streams (MQTT/AMQP/HTTP/OPC-UA), geofence events, detect threshold breaches (pressure drops, thermal anomalies), and trigger actions.
- Maintain asset telemetry history for trend analysis.
3) GeoAI & Analytics (ArcGIS Pro + Notebooks, ArcGIS Insights, Raster/ML tools):
- Train models for Remaining Useful Life (RUL), anomaly detection, risk scoring, fault localization, and demand forecasting.
- Use spatiotemporal statistics (hot spot, emerging hot spot) and graph analytics on network topology for criticality assessment.
- Fuse imagery/remote sensing (UAV, satellite, LiDAR) for vegetation encroachment, corrosion detection, or asset condition grading.
4) Operations & Work Management (ArcGIS Enterprise + Field Apps):
- Auto‑create work orders in EAM systems (SAP, Maximo, Infor) via integrations.
- Dispatch with ArcGIS Field Maps/Workforce/Navigator, capture as‑built edits, photos, sensor readings.
- Maintain digital twins’ dashboards with ArcGIS Experience Builder and Dashboards.
5) Governance & Security:
- Role‑based access, audit trails, data lineage, and quality checks (topology/attribute rules).
- High availability architecture and disaster recovery.
Priority Use Cases for Indian Utilities
Electric DISCOMs & Transmission
- Predictive asset health: Transformer failure risk from load, ambient temp, and insulation age; prioritizes replacements.
- Outage intelligence: Real‑time fault location from AMI meters and feeder sensors; critical customers and hospitals traced in seconds.
- Vegetation management: AI from imagery identifies growth near lines; crews targeted using proximity and risk score.
- Renewables integration: Solar/wind telemetry linked to network topology for curtailment analysis and grid stability.
Gas Distribution / O&G Pipelines
- Leak detection & localization: Pressure/flow anomalies mapped along pipeline segments with isolation trace to minimize impact.
- Cathodic protection monitoring: IoT potential readings analysed for corrosion risk; auto‑generated inspections.
- Right‑of‑way encroachment: Imagery + GeoAI flags construction near pipelines; incident triage via dashboards.
Water Utilities
- Non‑Revenue Water (NRW) reduction: Pressure transients and night‑flow anomalies detect hidden leaks; prioritized repair routes.
- Pump/valve health: Vibration + run‑hours predict RUL; spatial prioritization lowers energy cost and downtime.
- Quality incidents: Real‑time contaminant alerts traced downstream to affected consumers.
Telecom (Fiber/5G)
- Network assurance: IoT probe telemetry + topology traces identify fault domains; SLA‑aware routing.
- Asset lifecycle: Predictive maintenance for towers, cabinets, and fiber segments with work packages pushed to field apps.
Data to Decisions: A Typical GEO-AI/IoT‑Ready Workflow
- Model assets in ArcGIS Utility Network (domains, asset groups, types, rules, traces).
- Stream sensor data with Real‑Time / Velocity; store spatiotemporal events.
- Prepare features & labels (historical failures, inspections, weather hazards, demographics, imagery indices).
- Train GeoAI models (classification/regression/anomaly) using ArcGIS tools and notebooks.
- Score assets daily for health and risk; publish to feature services.
- Trigger actions: geofenced alerts, auto work orders, optimized crew scheduling.
- Close the loop: capture field results; retrain models with new evidence.
KPIs that Improve with Next‑Gen Asset Management
- SAIDI/SAIFI reduction (electric reliability)
- Leak rate/NRW (Non-Revenue Water)/methane intensity reduction (gas & &water)
- MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures) / unplanned downtime
- Work order cycle time first‑time fix
- Safety incidents near‑miss capture
- OPEX/Energy costs through targeted maintenance
- Customer satisfaction (fewer outages, faster restoration)
Implementation Roadmap (Phased, Low‑Risk)
Phase 0 — Readiness (4–6 weeks)
- Assess data, sensors, SCADA/AMI readiness; define priority use cases & KPIs.
- Stand up ArcGIS Enterprise landing zone; confirm Utility Network design.
Phase 1 — Foundation (8–12 weeks)
- Migrate or configure Utility Network; establish topology & rules.
- Connect initial IoT streams (pilot feeders/zones); basic real‑time dashboards.
Phase 2 — Analytics (6–10 weeks)
- Build feature engineering pipelines; train first risk/health models.
- Integrate with EAM/CMMS, automated work order creation.
Phase 3 — Scale & Optimize (ongoing)
- Expand sensors; improve models with feedback loops.
- Add imagery + LiDAR for condition grading; expand to renewables/telecom.
- Formalize governance, MLOps, and change management.
Architecture briefly (Esri‑centric)
- Data & Models: ArcGIS Pro/Enterprise, ArcGIS Utility Network
Conclusion
The convergence of AI, IoT, and GIS is transforming asset management from a reactive process into a proactive, predictive, and resilient strategy. By leveraging ArcGIS Utility Network as the digital foundation and integrating real-time IoT data with advanced analytics, utilities can achieve unprecedented reliability, operational efficiency, and sustainability.
This is not just a technology upgrade—it’s a strategic imperative for utilities to future-proof their networks, reduce risks, and deliver uninterrupted services to millions of consumers. Those who embrace this next-gen approach today will lead the way toward a smarter, safer, and more sustainable tomorrow.

M Raja Goud is a Technical Consulting Manager with expertise in utility & telecom GIS, and holds a certification in Esri ArcGIS Utility Network.
