As the world grapples with the complex challenges posed by urbanization, climate change, and resource depletion, the imperative for sustainable infrastructure development has never been more pressing. In this context, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies offers unprecedented opportunities to revolutionize the planning, design, construction, and management of infrastructure systems The challenges of rapid urbanization in India are multifaceted as well as interconnected, causing a domino effect on the urban services and utility networks, thus necessitating the demand for highly efficient, multi-hazard resilient, cost effective infrastructure. (Balasubramanian, S., 2024).
In the context of India, the failure of traditional urban planning often stems from a lack of democratic participation and a prevalent top-down approach, resulting in cities developing at a pace and in patterns that outstrip conventional planning capabilities (Ananya Roy, 2009). This leads to critical issues such as economic disparities, social inequality and exclusion, environmental degradation, overcrowding, housing shortages, and an overwhelming strain on existing infrastructure.
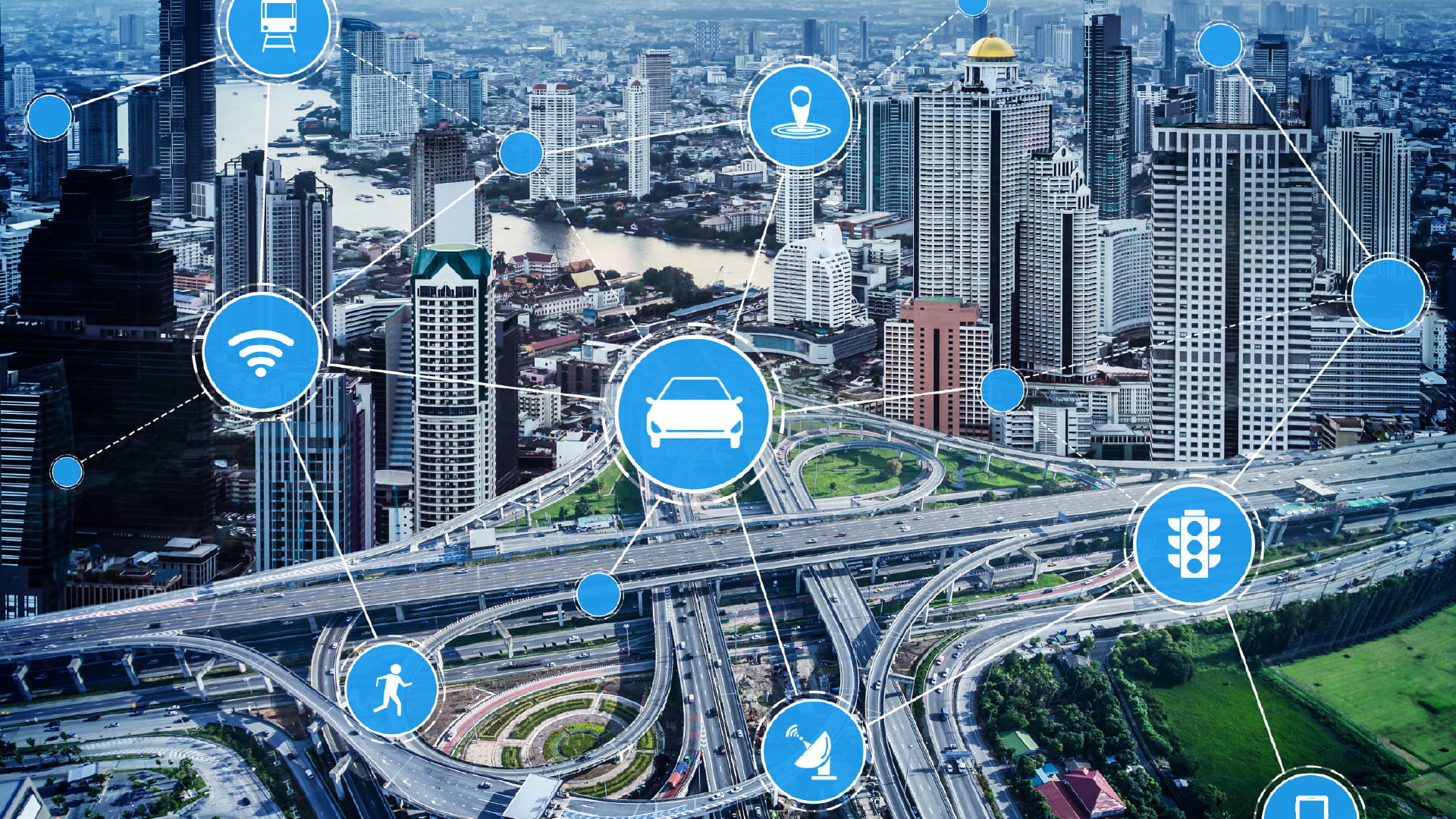
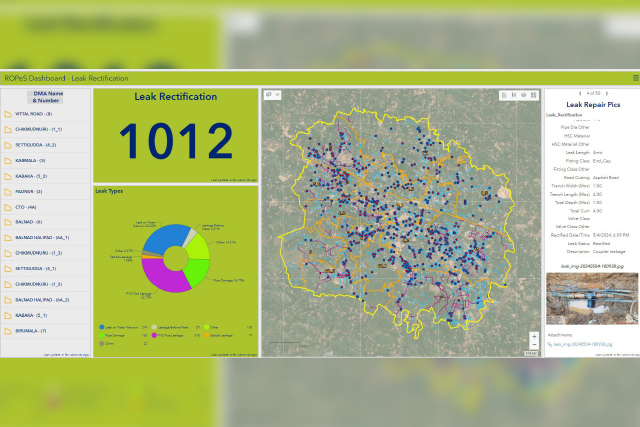
This paper examines the transformative potential of integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI), Geographic Information Systems (GIS), and the Internet of Things (IoT) – collectively, refined products of Big Data – to revolutionize urban infrastructure monitoring and management.
AI-enabled urban infrastructure monitoring uses AI technologies like machine learning and computer vision to design, manage, and optimize city systems, thus integrating diverse data from traffic, waste, energy, water, and safety networks (Setyadi and Jaya, 2025). In addition, AI-driven predictive analytics models have enabled early warning systems for earthquakes, floods and wildfires, facilitating proactive disaster preparedness and risk mitigation. (Bajwa, 2025). Integrating these with an AI-enabled monitoring system promises to transition urban planning from reactive problem solving to proactive, preventative strategies, fostering truly sustainable, resilient, cost-effective, and efficient infrastructure required for present and future generations (Rad, A. M. et. al., 2025).
The research outlines the effective integration of Geo Informatics with AI and IoT technologies, explores key methodologies for developing predictive infrastructure models, and investigates their contribution to multi-hazard resilience. It also critically addresses the ethical considerations associated with deploying AI for urban infrastructure, including data privacy, algorithmic bias, and equitable access to benefits.